Table of Contents
Once, Khalil Gibran said, “Beauty is not in the face; beauty is a light in the heart.” But what if you start to lose that beauty? What if you lose glowing skin as you age? What if your heart starts to feel burdened? Never should it happen. However, if you are not taking enough vitamin E, you might be on your way to such scares.
Indian culture and its Ayurvedic roots always focused on having a diverse diet that provides all essential nutrients. However, today, the fast-food culture has deprived us of the basics. We are not taking enough micronutrients, especially ‘Vitamin E’.
In this article, we’ll tell why exactly it is time we focus on vitamin E, its benefits, what Ayurveda says about it, and some risks involved. So, let’s see the significance of E.
What Ayurveda Speaks About Vitamin E?
Before modern science, humans had traditional medicine systems backed by ancient scientific knowledge that saw foods in a different light. Ayurveda, one of the oldest medicine systems, takes a holistic approach.
Although it doesn’t specifically mention vitamins A, B, C, or E (because these terms are given by modern science),
Ayurveda mentions various herbs and elements, their importance, effect and utility in our bodies. Aloe vera, cedarwood, and wheatgerm have been great examples of how our ancient sciences knew it all! [1]
Now, these foods are known to be rich sources of antioxidants and beneficial nutrients. And if we dive a bit more deeply, these substances contain compounds that modern science would classify as having vitamin E-like properties.
Vitamin E isn’t a single compound. It’s a family of eight molecules, each with slightly different properties and functions.
Now, let’s peel off some layers and see why Vitamin E is vital.
The Many Benefits of Vitamin E

Vitamin E was first discovered in 1922 by Herbert McLean Evans and Katharine Scott Bishop. Since then, the scientific scope has been continuously scanning it to know its beneficial depths. Here are some proven benefits that we get from vitamin E foods:
1. Brings the benefits of antioxidants
Antioxidants are the gems of the nutrient world. They protect against the damage-causing free radicals. The result? Protection against premature aging, diseases, weakness, etc.
Vitamin E is one of the few vitamins that also function as antioxidants [2]
A 2021 study showed that supplementing with vitamins E and C lowered oxidative stress. [3]
Read about the top antioxidant-rich food here!
2. Improves Gut Performance
Vitamin E, renowned for its antioxidant prowess, is crucial in bolstering gut health and optimizing gut performance. Its potent anti-inflammatory properties alleviate inflammation within the gastrointestinal tract, addressing conditions like inflammatory bowel issues.
Its antioxidant activity combats oxidative stress, safeguarding gastrointestinal tissues from damage. Incorporating vitamin E-rich foods like nuts, seeds, leafy greens, and vegetable oils into the diet can fortify gut health. At the same time, supplementation may offer targeted support for specific gut-related conditions under the guidance of a healthcare professional. [4]
3. Pumps Up Immunity
Vitamin E is not just your well-wisher but also a superb supporter when it comes to your immunity. It is known to stimulate and strengthen the army of white blood cells, our infection-fighting cells. [5]
Furthermore, it improves resistance to viral infections and enhances the immune response to vaccines. [6]
4. Protects Brain Functioning
Our grandma’s always told us to have almonds for a great brain!
Vitamin E plays a role in protecting against neurodegeneration. With time, it prevents age-related memory and brain-functioning issues. This happens due to its ant-oxidative properties. [7]
Aging can either be painful or graceful. It depends on how we nourish our bodies at a young age. Most people start forgetting things as they age. This hampers the joy of life.
5. Gives you radiant skin
Vitamin E is great for your skin! It’s like a superhero that fights off bad stuff and keeps your skin healthy and glowing. It is super moisturizing, which helps keep your skin soft and hydrated. It locks in moisture and prevents your skin from getting dry and flaky.
The antioxidants protect your skin from damage caused by harmful molecules called free radicals. This helps to prevent wrinkles, fine lines, and other signs of aging.
It also has healing and protective properties that can help to repair damaged skin and act as a protective barrier for your skin, shielding it from environmental stressors like pollution and UV rays. Whether you have a sunburn, a scar, or irritated skin, vitamin E can help to soothe and heal it.
6. Helpful for the Heart
The heart is the most vital organ of our body. Also, it is the most suffered organ around the world. Vitamin E is one of the many nutrients that ensure our hearts stay healthy and happy.
High BP, high triglyceride level, and high LDL – these are the villains behind heart issues. Studies have shown that having enough vitamin E can help keep these bad guys away. [8]
7. Supports Eyesight
Indeed, what a wonderful world, and to keep seeing its beautiful colors as we age, we must take enough vitamin E. This eye-focused nutrient provides added antioxidant protection in the eyes. Studies show that vitamin E may help prevent cataracts by reducing oxidative stress and slowing age-related lens opacification. [9]
And know what? One great way to increase its levels in the eye is to support it with vitamin E consumption. This is because,
Vitamin C in the eye can even regenerate other antioxidants such as vitamin E. [10]
So, as we see the importance of vitamin E in our lives, it is time to see the many food items that stay high in it.
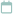
Vitamin E Foods
You don’t need to go to the market to have vitamin E. A mere look around the kitchen and you’ll find yourself floating in a sea of options. Here is a glimpse
I. Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds don’t just bless us with healthy fats (unsaturated fats), but they are also an excellent source of vitamin E. Here are some options you can cherish during your snack time:
Nuts and Seeds high in Vitamin E
| Name | Per 1 ounce (28.34 grams) | Per 100 grams |
| Sunflower seeds [11] | 10 mg | 35 mg |
| Almonds | 7.3 mg | 26 mg |
| Hazelnuts | 4.3 mg | 26 mg |
| Pine nuts | 2.7 mg | 9.3 mg |
| Peanuts | 2.4 mg | 8.3 mg |
| Brazil Nuts | 1.6 mg | 5.7 mg |
| Pistachios | 0.8 mg | 2.9 mg |
| Pumpkin seeds | 0.6 mg | 2.2 mg |
II. Cooking Oils & Ghee
Cooking oil is often looked down on for its high fat content. In truth, our bodies need fat to function well. The problem lies with the fat selection. We often consume bad fat (trans and saturated), which leads to problems.
Choosing good fat can improve our health. It can even reduce bad cholesterol in our bodies. Consuming in balance is the key here.
Now, here are cooking oils that offer high vitamin E content:
Cooking oils high in Vitamin E
| Name | 1 tablespoon | Per 100 grams |
| Wheat germ oil | 20 mg | 149 mg |
| Hazelnut oil | 6.4 mg | 47 mg |
| Sunflower oil | 5.6 mg | 41 mg |
| Almond oil | 5.3 mg | 39 mg |
| Cottonseed oil | 4.8 mg | 35 mg |
| Safflower oil | 4.6 mg | 34 mg |
| Rice bran oil | 4.4 mg | 32 mg |
| Grapeseed oil | 3.9 mg | 29 mg |
Vitamin E acts as a natural antioxidant, It protects healthy fats from damage and extends the shelf life of certain foods.
III. Vegetables & Greens
Not just for vitamin E, but we must embrace vegetables for their overall benefits. They must be a part of your daily diet. One big benefit is that consuming vegetables increases lifespan.
Vegetables high in vitamin E
| Name | Per 100 grams |
| Red sweet pepper | 1.6 mg |
| Turnip green | 2.9 mg |
| Beet greens | 1.8 mg |
| Butternut squash | 1.3 mg |
| Broccoli | 1.5 mg |
| Mustard greens | 1.8 mg |
| Asparagus | 1.5 mg |
| Swiss chard | 1.9 mg |
| Spinach | 2.0 mg |
IV. Fruits
Fruits, although healthy, must still be consumed in moderation. This is because most fruits stay high in simple sugars. The best way to cherish fruits is to eat those containing complex carbs.
Fruits are an excellent source of several vitamins and minerals. Here are some high in E:
Fruits high in vitamin E
| Name | Per 100 grams |
| Avocado | 2.1 mg |
| Mango | 0.9 mg |
| Kiwifruit | 1.5 mg |
| Blackberries | 1.2 mg |
| Black currants | 1 mg |
| Cranberries | 2.1 mg |
| Olives | 3.8 mg |
| Apricots | 0.9 mg |
| Raspberries | 0.9 mg |
V. Other Foods Rich in Vitamin E
Apart from the above-given foods, if you crave eating meat too, there are plenty of options to please your hunger and vitamin-E-need.
Fruits high in vitamin E
| Name | Per 100 grams |
| Abalone | 4 mg |
| Goose meat | 1.7 mg |
| Atlantic salmon | 1.1 mg |
| Rainbow trout | 2.8 mg |
| Snails | 5 mg |
| Crayfish | 1.5 mg |
| Fish roe | 7 mg |
| Octopus | 1.2 mg |
| Lobster | 1 mg |
| Cod | 2.8 mg |
The wisdom lies not in depending on one food alone but in having a diverse diet. Try to include little of everything and you’ll rarely face any adverse effect.
Tips & Tricks for Maximizing Vitamin E Intake
Eating a certain amount of vitamin E does not equal your overall intake. For example, if you consume certain food having 10mg of vitamin E in its raw form, your body might be able to get only 5mg due to certain factors such as wrong cooking techniques, improper absorption, certain disorders, etc.
Here are some ways to maximize your vitamin E intake:
- Say no to heat – Vitamin E is heat-sensitive. Exposing it to high temperatures can damage it. So, avoid deep frying. The best way is to steam, stir-fry, or poach your veggies. Also, keep the cooking temperatures low whenever possible.
- Choose the right oil – Why not choose oils that are already rich in Vitamin E? Some examples include sunflower, safflower, and wheat germ oil. This is a great way to boost your intake. But, as seen above, you must try to heat the oil too much. The best way is to drizzle these oils after cooking to retain their full benefits. Or simply use these as your salad dressing. Again, if you want to go for high-heat applications, choose oils with higher smoke points like peanut or avocado oil.
- Don’t over-roast nuts and seeds – If you love eating roasted nuts, opt for dry roasting at lower temperatures (around 300°F). And just when you see getting too brown, stop!
- Combine with healthy fats – Vitamin E is fat-soluble. It dissolves and absorbs better in the presence of dietary fats. But don’t choose any fat. Instead, embrace healthy fats like olive oil, nuts, seeds, avocados, fatty fish etc.
- Another ingredient that you should include for Vitamin E intake is curd.
And now about storage.
Because vitamin E is heat-sensitive, it can lose its potential over time. So the best way is to shield these oils from light and heat. Use airtight containers. You may even refrigerate oils once opened. Because oils like wheat germ oil lose their Vitamin E content quickly once opened.
When buying nuts, keep their quantity smaller to ensure that you get them as fresh as possible. They too come with an expiry date.
How Much Vitamin E per day?
For people aged 14 years or more, the recommended intake of vitamin E is 14 mg per day (irrespective of gender). However, lactating mother might need to go up a bit to 19 mg per day. For people aged less than 14, here is the right dosage:
| Age[12] | Male | Female |
| 0–6 months | 4 mg | 4 mg |
| 7–12 months | 5 mg | 5 mg |
| 1–3 years | 6 mg | 6 mg |
| 4–8 years | 7 mg | 7 mg |
| 9–13 years | 11 mg | 11 mg |
| 14+ years | 15 mg | 15 mg |
When to go for supplements?
Sometimes you might need to go for a higher amount of vitamin E due to certain reasons. For example,
- if you suffer from a disorder that requires a higher dose, or
- if you are unable to get it from natural foods
In these cases, you may always consider going for a vitamin E supplement. However, always consult a doctor in these scenarios.
Conclusion
Vitamin E is one of the most ignored nutrients. Nevertheless, its importance is irreplaceable. From protecting against oxidative stress to supporting immune function and enhancing brain health, the benefits of vitamin E are exceptional. Not just his, but it also helps in helping heart and eyes as well.
The best way to ensure the recommended vitamin E intake is to incorporate natural vitamin E-rich foods. Nuts, seeds, oils, vegetables, fruits, and certain meats such as goose meat, all these foods are great sources of vitamin E.
Remember to optimize your intake by choosing cooking methods that preserve vitamin E content. It is heat-resistant and gets damaged at high temperatures.
So, let’s power up our plates with these E-enriched foods and pave the way to a healthier and happier life. Because an eye for an E makes the whole world healthy.
FAQs
Yes, vitamin E can be taken daily as part of a balanced diet or as a dietary supplement. The recommended daily intake for adults is 15 mg. However, consulting with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen is essential.
Yes, Omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin E can be taken together. They complement each other well in promoting overall health. Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for heart health, brain function, and reducing inflammation, while vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that protects cells from damage caused by free radicals. However, following recommended dosages and consulting with a healthcare provider is advisable.
Both fish oil and vitamin E offer unique health benefits. Fish oil, rich in Omega-3 fatty acids, is renowned for its heart-healthy properties, supporting brain function, and reducing inflammation just like Vitamin E. The choice between fish oil and vitamin E depends on individual health goals and dietary needs. It’s best to incorporate nutrient-rich foods and supplements into your diet for optimal health benefits.
Symptoms of a vitamin E deficiency may include muscle weakness, vision problems, impaired coordination and balance, nerve damage, and anemia. Additionally, vitamin E deficiency can contribute to compromised immune function and an increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
Vitamin E deficiency can lead to various health problems, including muscle weakness and vision problems. Its deficiency may increase cardiovascular disease risk due to its protective role against oxidative stress and inflammation.