Table of Contents
Prawns are more than just seafood or a freshwater option; they are an excellent choice as part of the food group that provides essential nutrients for a balanced diet.
They could also offer a unique blend of omega-3 fatty acids, high-quality protein, and essential nutrients for every diverse dietary habit of India’s regions.
Learning about the nutritional profile of prawns might help you gain a better understanding of how they may benefit heart and bone health and thyroid function, among other things.
If you’re a general food enthusiast, a person who is mindful about health, or somebody exploring marine nutrition, this article covers all the aspects of why prawns should be in your diet.
Nutritional Profile of Prawns
Prawns come in many varieties, but their nutritional content is very similar, with minor variations in their composition. One of the major commercial prawn species worldwide is, for example, Penaeus indicus, the Indian white prawn [1] [2].
Nevertheless, in this section, we will discuss the nutritional content of three common prawn varieties, namely Macrobrachium rosenbergii (giant freshwater prawn), small Macrobrachium sp., (Small Prawns) and Macrobrachium sp. (Tiger prawns).
Knowing their nutritional profiles will help you make informed choices about including them in your nutritional plan.
Also, Aashirvaad helps you to validate the correctness of your fibre requirement by offering a quick assessment through the ‘My Meal Plan’ test for holistic and overall balanced meal intake. You will also receive tailored meal plans that will satisfy your hunger and fulfill your daily fibre requirements.
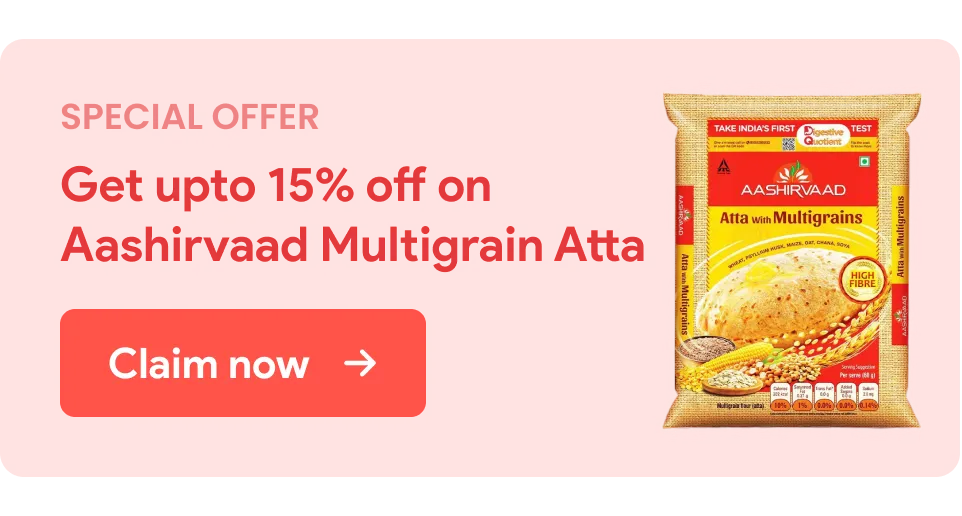
Here’s a detailed look at what 100 grams of prawns may offer [3]:
| Macrobrachium rosenbergii (Big) | Macrobrachium sp. (Small) | Macrobrachium sp. | |
| Common Name | Giant freshwater prawn | Small prawn | Tiger prawns |
| Protein (g) | 19.24 | 13.0 7 | 14.24 |
| Total Fats (g) | 0.52 | 0.78 | 0.66 |
| Energy (KCal) | 90.8 | 70.9 | 67.8 |
| Vitamin B6 (mg) | 186 | 207 | 216 |
| Vitamin B9 (Total Folates) (µg) | 1826 | 1306 | 1875 |
| Calcium (mg) | 48.55 | 67.99 | 57.90 |
| Iron (mg) | 0.78 | 0.87 | 0.84 |
| Magnesium (mg) | 39.25 | 26.91 | 22.94 |
| Sodium (mg) | 849 | 77.71 | 80.77 |
| Zinc (mg) | 1.44 | 0.87 | 1.02 |
Health Benefits of Prawns
Prawns have a range of health benefits suited to the dietary requirements of many people. They are so delicious to consume, and they come loaded with potential benefits that could be good for your health.
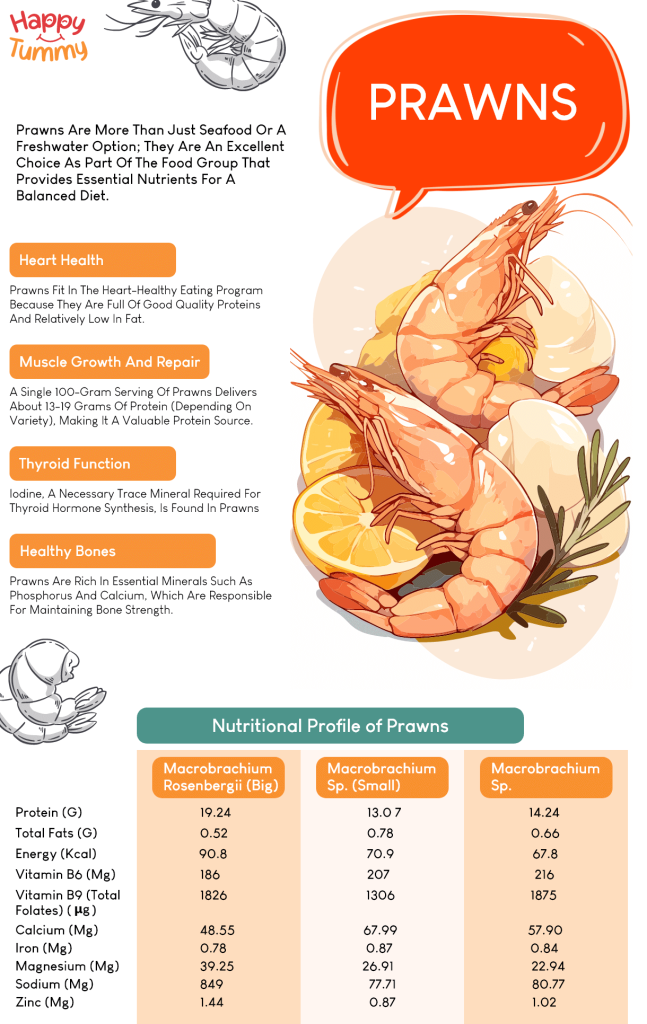
In the summary below, you can see how prawns may benefit various health aspects:
1. Heart Health [4]
- Prawns fit in the heart-healthy eating program because they are full of good quality proteins and relatively low in fat. Most of the fats come from polyunsaturated sources, which are usually considered ideal for a well-balanced diet.
- Prawns contain omega-3 fatty acids, which might help improve heart health and could be associated with maintaining healthy blood pressure levels. The omega-3 fatty acids have Anti-inflammatory and Anti-coagulant properties and may help to reduce the risk of Atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular diseases [4].
- Including seafood like prawns in your diet might be linked to better heart health, especially for those who are more vulnerable, such as middle-aged individuals with type 2 diabetes [5].
A heart-healthy diet is all about balance. Hence, pairing prawns with nutrient-dense chapatis made from flour like Aashirvaad Multi Millets Mix Aata may enhance your meals with additional fiber and protein.
The blend of millets such as jowar, bajra, and ragi might complement the omega-3 benefits of prawns, offering a wholesome approach to maintaining better heart health.
2. Muscle Growth and Repair
- Proteins are formed by amino acids, which serve as the small building blocks critical for cell structures and energy [6].
- Indian diets can, at times, be deficient in certain amino acids, lysine being a prominent one, so this high-quality protein source may help in fulfilling this gap
- A single 100-gram serving of prawns delivers about 13-19 grams of protein (depending on variety) [7], making it a valuable protein source.
- Prawns majorly contain almost all the vital amino acids the body cannot synthesize and need to help build and repair muscle [8].
- For example, A study conducted on the Evaluation of the Nutritional quality of cultured prawns evaluated that 19 amino acids were found in the giant freshwater prawns (Macrobrachium rosenbergii), of which 11 are essential and 8 are non-essential [9].
3. Thyroid Health
- Iodine, a necessary trace mineral required for thyroid hormone synthesis [10], is found in seafood like prawns [11].
- Adequate iodine intake is known to be a necessary prerequisite for proper thyroid functioning, an organ system that exerts considerable regulatory control over our metabolic rate and health.
4. Healthy Bones
- Prawns are rich in essential minerals such as phosphorus and calcium [13], which are responsible for maintaining bone strength.
- Moreover, calcium is vital for blood clotting, muscle contraction and several metabolic processes [14].
- Some studies conducted have shown positive associations between fish and shellfish, such as prawn consumption and better bone health, especially for men and postmenopausal women aged 50 and older [15].
The gastrointestinal system bacteria is also studied to influence bone density and strength. For example, some dietary fibres could modify gut bacteria that may improve calcium absorption, an important factor for bone health.
Similarly, some studies also suggest a relationship between a healthy gut microbiome and better bone density, which might lead to decreased risk of bone disorders such as osteoporosis [16] [17].
A healthy gut is vital to how well your body can absorb the nutrients it needs, and bone strength relies heavily on nutrient absorption.
In that sense, the Aashirvaad Digestive Quotient test will help you quickly understand your digestive health and how to care for it. So, knowing your score on a scale of 1 to 100 can assist you in making dietary decisions that will keep your bones strong as well as stay healthy.
Nutritional Health Benefits of Prawns[18]
- Prawns are a very good source of vitamins B1 (thiamine) and B2 (riboflavin), which may help promote energy metabolism, boost skin health and repair, and maintain healthy eyes.
- Regular consumption of prawns can provide a good amount of minerals namely sulfur, calcium and phosphorus. Sulfur is also present in sulfur-containing amino acids namely methionine, cysteine, and taurine, all found in prawns, and are essential for health.
- Sulpfur is also a constituent of Vitamin B1, biotin, and glutathione, an important antioxidant that protects cells. This mineral may also help with the formation of skin, hair, nails, and cartilage.
- Other nutrients prawns provide are sodium, potassium, zinc, and selenium. These minerals play a variety of roles in the body, from supporting immune function to managing cellular processes.
Therefore, incorporating prawns into your regular diet may help you get the nutrients in adequate quantities that are imperative for overall health, such as stronger bones, better energy metabolism, and improved immune function.
If you are unsure of the best way to plan a diet containing prawns, consult a dietician for reliable advice.
Conclusion
Prawns could be a great option for those who wish to add high-quality and a variety of nutrients to their meal. Studies show how they contribute to cardiovascular health and the immune system with essential nutrients and minerals such as zinc or selenium.
The article describes how prawns are not only an indulgent food but also are an excellent healthy choice for anyone looking to add more versatile varieties of seafood options to their diet.
With an overall balanced diet, you can enjoy the benefits that prawns provide (when you include quality sources and maintain moderate consumption) while staying in line with a larger picture of your dietary goals. ICMR recommends that people should consume food items from at least 5–7 groups daily [19].
To sum up, prawns could be your healthy food choice, whatever diet or nutritional requirements you may have.
FAQs
It is suggested that you avoid eating prawns if you get a strong, foul smell or if you detect any green or blue unwanted compounds on them. This can mean that they are spoiled, and consuming them could lead to foodborne illnesses. It is advisable to thoroughly wash and cook them before consuming and always source them from clean, unpolluted waters.
Do consult a healthcare professional to understand if you have any allergic reactions towards prawns and avoid consuming them, if present.
ICMR NIN Dietary guidelines recommend consumption of 30g of Fish & fleshy foods as a part of a balanced diet every day.
Hence you may consume prawns as a part of your diet in combination with other meat products to bring in diversification and variety.
Although Prawns have a favourable Omega 3: omega 6 ratio, they also have moderately high amounts of cholesterol, hence, it is always advised to consult with your nutritionists or healthcare providers and choose an individualized approach for balancing your intake and understanding your needs better.
Yes, prawns might help build muscle as they are rich in protein. With up to approximately 13–19 grams of protein per 100 grams, prawns have the potential to promote satiety and support muscle mass gain.
But to gain optimal benefits on muscular growth, one should have other foods as well to get the full spectrum of amino acids necessary for our body.