Table of Contents
We all want to walk stronger and larger in our lives, with veins full of energy and eyes sparkling with joy. But sometimes the picture turns grim. There are days when our shoulders fall, legs become heavy, and eyelids fall in the weight of weakness. Low energy! Body’s battery almost gone!
Sometimes, feeling low on energy for a short span is all fine. But when it carries itself for days and days, it is a problem. And this problem must be dealt with. Chronic fatigue and weakness could be foreboding a more serious thing.
Although there could be many reasons behind low energy, nutrient deficiency is one of those. Today, we’ll be looking at just that.
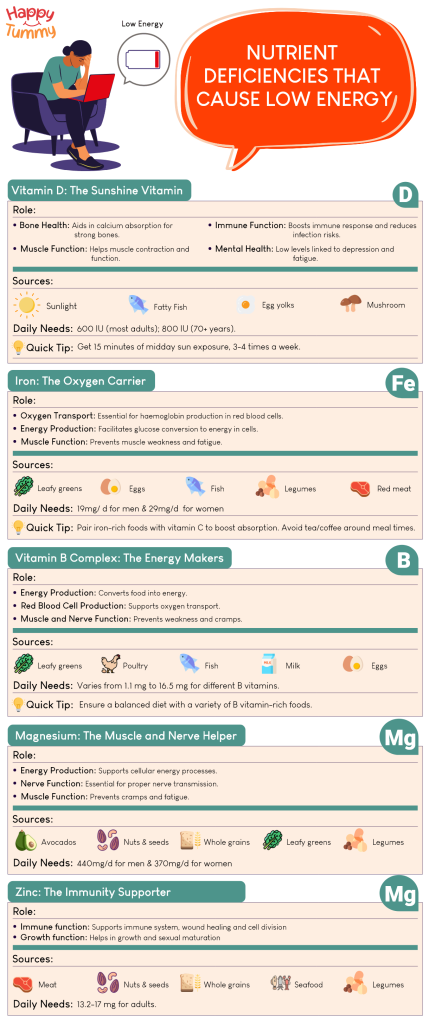
Here is a list of nutrients that might be causing low energy:
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is the juice of the sun. This also gives it the name ‘Sunshine Vitamin’. But why vitamin D? And what is its role in fatigue?
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient that our bodies can produce naturally. But it only happens when we take a sunbath. When exposed, our bodies synthesise the UV B into previtamin D3 and then D3.
Talking about foods rich in vitamin D – there aren’t many. Here are a few foods that provide some amounts of vitamin D –
- Egg yolk
- Mushrooms
- Sea Food – tuna, cod, herring, sardines, fatty fish, etc.
- Vitamin D-fortified foods
Vitamin D plays a big role in several body functions such as:
Bone Health – The usual belief that vitamin D makes our bones stronger is half the truth. It is indirectly related. Vitamin D helps in better absorption of calcium, which is what makes our bones stronger. The better our bodies can absorb calcium, the stronger our bones become.
Immune Function – Vitamin D also boosts our immune system. Studies have shown now and then that inadequate intake of vitamin D leads to poor immunity and more infections. [1]
Muscle Function – Vitamin D makes us muscular? No! Rather, it makes them function smoothly. There are vitamin D receptors present in our muscles that help our muscles contract and flex when needed. A lack of proper muscle functioning can make you fall, as happens in very old age. [2]
Mental Health – More and more studies are bridging the gap between vitamin D deficiency and an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline. A fall in vitamin D means a fall in mood, and a fall in mood means a sense of fatigue.
Now, here is how all these things together make our bodies weaker –
Lesser bone density leads to weakened bones, which creates difficulty walking. This gets worse with the weakening of muscle functioning. Furthermore, fallen immunity invites more diseases, which causes hidden weakness due to the body regularly fighting with pathogens. And lastly, when the brain fails to function well, it fails to release hormones well. Consequently, the human body suffers.
How Much Vitamin D Do We Need?
According to the Indian dietary guidelines provided by ICMR-NIN ,
- The recommended daily allowance of Vitamin D is 15mcg(600IU) per day for both men & women.
- For adults >70 years 20 mcg (800 IU) of Vitamin D
- The number is 400 IU per day for infants and babies.
How To Get Enough Vitamin D?
Because there are not enough foods that you can reap vitamin D from (except some fish, mushrooms, and vitamin D-fortified foods), the next best solution is to get it from sunlight.
To get vitamin D, don’t expose your skin to sunlight for long. It can cause skin burns and other skin issues. The best time to get vitamin D from the sun is not early morning or late evening. Rather, it is noon.
Contrary to the belief, the best time to get enough vitamin D is noon, when the sun is at its peak. At this time, the UVBs are more intense. 15 minutes a day, 3-4 times a week, can help you have enough vitamin D. [3]
Otherwise, go for supplements.
Iron
Of course, because iron anyhow resembles strength, a lack of iron should mean weakness. No!
A lack of iron in our bodies surely leads to weakness, but the ‘why’ behind this is a bit different.
We need iron because it helps in the transportation of oxygen to each tiny corner of our bodies. Here is the cycle:
- Iron helps in the production of haemoglobin (protein in our red blood cells)
- Haemoglobin carries oxygen throughout our bodies using blood
- A lack of iron leads to a lack of haemoglobin, which in turn leads to a lack of oxygen
And when oxygen levels fall, fatigue and tiredness arrive uninvited.
Iron deficiency leads to a condition called anaemia
Furthermore, during metabolism (chemical reactions in our bodies to convert food into energy), oxygen is required when cells convert glucose into energy. Less oxygen, thus, leads to less energy production. We feel tired. This same happens in the case of muscles.
Muscles require a constant supply of energy to contract and function optimally. Due to compromised oxygen, muscles become weaker and tire more easily.
How Much Iron Do We Need Per Day?
The ICMR-NIN RDA for iron depends on various factors such as gender, physical activity levels, and physiological conditions such as during pregnancy, lactation, etc. Here’s a detailed guide on the recommended iron per day
| Age Group | Iron(mg/d) |
| Men | 19 |
| Women | 29 |
| Pregnant women | 27 |
| Lactating women (0-12months) | 23 |
| Infants (6-12months) | 3 |
| Children (1-3 years) | 8 |
| Children (4-6 years) | 11 |
| Children (7-9years) | 15 |
| Boys (10-12y) | 16 |
| Girls (10-12y) | 28 |
| Boys (13-15y) | 22 |
| Girls (13-15y) | 30 |
| Boys (16-18y) | 26 |
| Girls (16-18y) | 32 |
How To Get Enough Iron?
Unlike vitamin D, iron can be normally obtained from common day-to-day foods. [5]
- Iron-rich foods include red meat, fish, eggs, lentils, beans, whole grains, and products made from these foods.
- Leafy green vegetables are also a great source of iron.
However, the absorption of iron from these vegetables is slightly low. But this can be enhanced through proper intake of vitamin C.
Intake of vitamin C enhances iron absorption [6]
So, consume vitamin C-rich foods or beverages with iron-rich foods.
Examples of vitamin C-rich foods include citrus fruits, gooseberries (amla), and guava.
Note that tea, coffee, and some minerals can hamper your iron absorption. So, avoid sipping these at the same time as iron-rich foods and at least 1 hour before or after your meals.
If you can’t get enough iron from food, take help from supplements. But before you do this, consult once with a doctor first.
Vitamin B
B stands for beauty, but here it stands for strength. A lack of vitamin B leads to weakness. Vitamin B is a group of substances that are collectively called B Complex. Vitamin B complex includes
- Vitamin B1 – Thiamin
- Vitamin B2 – Riboflavin
- Vitamin B3 – Niacin
- Vitamin B5 – Pantothenic Acid
- Vitamin B6 – Pyridoxine
- Vitamin B7 – Biotin
- Vitamin B9 – Folate
- Vitamin B12 – Cyanocobalamin
However, not all B vitamins lead to weakness and low energy. A deficiency of vitamin B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, B12. But why does vitamin B deficiency lead to weakness?
The link with oxygen – Similar to iron, both vitamin B12 and folate support the production of healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells carry oxygen. This deficiency is also called anaemia, but megaloblastic anemia.
The link with energy production – B vitamins, including B12, B6, and B1 (thiamine), play crucial roles in converting food into energy. A deficiency of these vitamins means hampered energy production. This further means low energy.
The link with muscle functioning – Vitamin B1 (thiamine) supports smooth muscle function, and a deficiency can lead to muscle weakness, cramps, and pain.
A very low level of vitamin B1 leads to BeriBeri, a condition with weakness, loss of appetite, burning feet, etc. [7]
How Much Vitamin B Per Day?
The ICMR-NIN RDA depends on various factors such as Gender, physical activity levels, and physiological conditions such as during pregnancy, lactation, etc.
| Nutrient | Men | Women |
| Thiamine (mg /d) | 1.4-2.3 | 1.4-2.2 |
| Riboflavin (mg /d) | 2.0-3.2 | 1.9-3.1 |
| Niacin (mg /d) | 14-23 | 11-18 |
| Vit B6 (mg /d) | 1.9-3.1 | 1.9-2.4 |
| Folate (µg /d) | 300 | 220 |
| Vit B12 (µg /d) | 2.5 | 2.5 |
Note that vitamin B supplements must always be taken after consulting with your doctor and proper body check. Overdosing on these might lead to several issues. Also, pregnant women might require more of these vitamins.
How To Get Enough Vitamin B?
The best way to get vitamin B is to reap it from natural foods. Some common foods rich in vitamin B are leafy vegetables, eggs, milk, legumes, yoghurt, pork, chicken, salmon, etc.
If you are not able to meet your needs, you may go for supplements, but only after proper consultation.
Magnesium
The last nutrient that may lead to low energy levels is magnesium. Magnesium is a mineral, and our bodies utilize it in hundreds of biochemical reactions and functions. A few of these are
- Energy production
- Muscle contraction
- Nerve transmission
A lack of magnesium can lead to hundreds of body problems, such as high BP, heart issues, liver damage, infections, tooth cavities, etc.
A few of the many effects of magnesium deficiency are cramps, muscle weakness, and low energy. [8]
Magnesium helps convert food into energy and is essential for the proper functioning of mitochondria, which is called the “powerhouse” of cells. Also, it is an important mineral that helps in electrolyte balance. An electrolyte imbalance leads to fatigue, weakness, and low energy.
How Much Magnesium We Need Per Day?
The ICMR-NIN RDA for magnesium depends on various factors such as gender, physical activity levels, and physiological conditions such as pregnancy, lactation, etc. The present daily magnesium requirement is presently set at these values:
| Life Stage/Gender | RDA Magnesium (mg)/ day |
| Adult Men | 440 |
| Adult Women | 370 |
| Pregnancy | 440 |
| Lactation | 400 |
However, know that overtaking magnesium can lead to harmful symptoms, too.
How To Get Enough Magnesium?
The best way to get magnesium is to eat foods rich in magnesium. It must be consumed naturally. Here are foods that are high in magnesium:
- Avocados
- Nuts and Seeds
- Legumes
- Tofu
- Whole grains
- Bananas
- Leafy green vegetables
- Fatty fish
You can easily get enough magnesium naturally from food. However, if you still need to get enough, supplements can be reached after proper consultation.
Zinc
Zinc deficiency can lead to various health issues due to its critical roles in the body. Zinc supports the immune system, wound healing, and cell division. It also acts as an antioxidant, helping to fight off damaging free radicals.
Symptoms of zinc deficiency can vary but often include impaired immune function, delayed wound healing, hair loss, and loss of appetite.
In children, it can lead to growth retardation and delayed sexual maturation. Pregnant women and older adults are also at higher risk of deficiency due to increased zinc needs or reduced absorption.
How Much Zinc We Need Per Day?
The ICMR-NIN RDA for Zinc depends on various factors such as Gender, physical activity levels, and physiological conditions such as pregnancy, lactation, etc
| Life Stage/Gender | RDA ZINC (mg/d) |
| Adult Men | 17 |
| Adult Women | 13.2 |
| Pregnancy | 14.5 |
| Lactation | 14.1 |
How To Get Enough Zinc?
Include zinc-rich foods in your diet, such as:
- Meat: Beef, lamb, pork, and poultry.
- Seafood: Oysters, crab, lobster, and shrimp.
- Dairy: Milk, cheese, and yogurt.
- Plant-based: Legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas), nuts, seeds (pumpkin seeds), and whole grains (wheat germ).
Opt for cooking methods that preserve zinc content, such as steaming or microwaving vegetables instead of boiling, which can leach out zinc.
The Bottom Line
The feeling of low energy and weakness is one of the worst feelings in the world. Although there are numerous reasons behind low energy, nutrient deficiency is a big one.
A lack of vitamin D, iron, vitamin B, magnesium, and vitamin C is directly related to low energy levels and fatigue. The reason is their link to oxygen transportation, immunity support, bone support, and muscle functioning.
It is important to get these vitamins naturally from foods. However, if you can still not meet your basic RDA for these nutrients, supplements can be taken after proper consultation.
FAQs
A deficiency of vitamins D, C, and B has been directly linked to a feeling of low energy and fatigue. They can make your body lack oxygen, bone strength, and exercise tolerance.
There are numerous reasons behind low energy, such as nutrient deficiency, chronic illness, stress, depression, dehydration, poor sleep, caffeine withdrawal symptoms, etc.
Lacking vitamin D, C, B, iron, and magnesium over a long period can lead to chronic fatigue. However, one must ensure the intake of all nutrients possible.
Feeling tired and unmotivated could be a result of poor sleep, nutrient deficiency, depression, dehydration, illness, etc. It is best to consult a doctor.