Table of Contents
Health and wellness are vast topics, and they have many different aspects. Once you get into a discussion related to health, there is a lot that one can talk about. One such vital topic is inflammation foods.
Inflammation is your body’s way of responding to a problem. Not many of us may know it. However, everyone needs to understand how our lifestyle can positively and negatively impact inflammation.
But, it is a simple way in which your body tells the immune system something is wrong and it’s time to fight the infection. So, what’s an example of inflammation?
You ate something wrong and had diarrhea; that can be one reason for the inflammation, but not all diarrhea is inflammatory. Another typical example to understand is when you twist your ankle, and there is swelling, again, inflammation. Our bodies need natural/acute inflammation, or survival won’t be easy.
However, inflammation and chronic inflammation are two different things. In some respects, normal inflammation is healthy, whereas chronic inflammation can damage tissues, healthy cells, and organs. So, let’s discover more about inflammation.
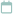
Top Food that Causes Inflammation
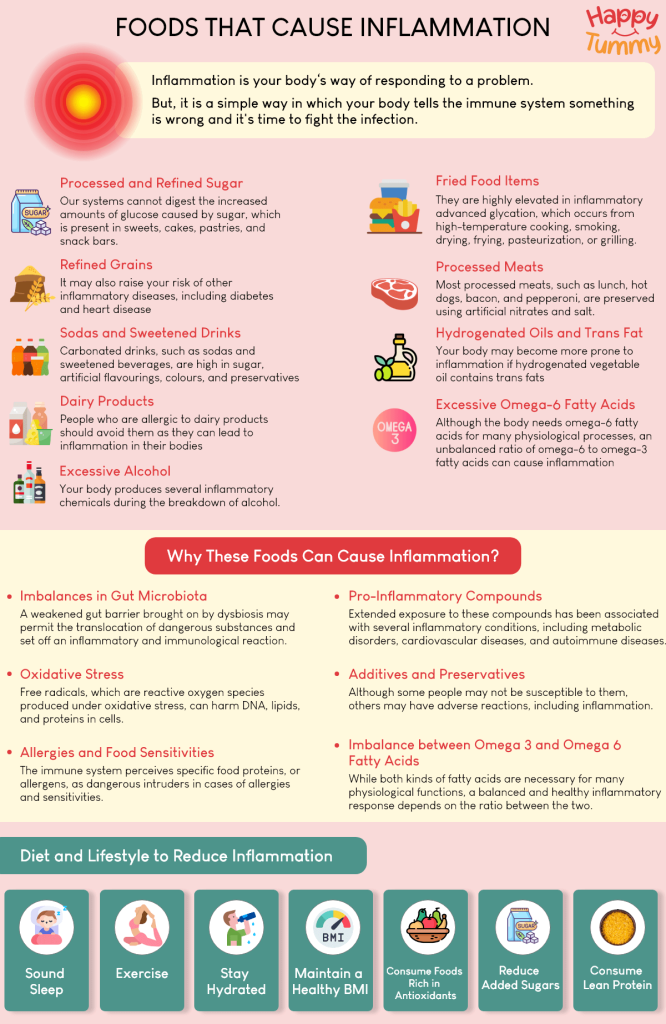
Here are some food products that cause inflammation in our bodies:
1. Inflammation Foods – Processed and Refined Sugar
It should come as no surprise that sugar tops the list [1]. Our systems cannot digest the increased amounts of glucose caused by sugar, which is present in sweets, cakes, pastries, and snack bars. As a result, the body produces more pro-inflammatory cytokines, which raise inflammation levels.
2. Inflammation Foods – Fried Food Items
Another food product that might cause inflammation is fried food [2]. They are highly elevated in inflammatory advanced glycation, which occurs from high-temperature cooking, smoking, drying, frying, pasteurization, or grilling.
3. Inflammation Foods – Refined Grains
Higher blood levels of inflammation have been related to refined grains, which are detrimental not just to arthritis but may also raise your risk of other autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, including diabetes and heart disease [3].
4. Inflammation Foods – Processed Meats
Most processed meats, such as lunch, hot dogs, bacon, and pepperoni, are preserved using artificial nitrates and salt. These meats are also generally heavy in saturated fat. Regularly using processed meats has been associated with an increased risk of inflammation, which many believe results from nitrates and saturated fats [4].
5. Inflammation Foods – Sodas and Sweetened Drinks
Carbonated drinks, such as sodas and sweetened beverages, are high in sugar, artificial flavourings, colours, and preservatives. It is believed to trigger inflammation because they contain a lot of sugar [5]. Furthermore, consuming large amounts of soda and sweetened drinks with added sugar raises the risk of inflammatory disorders like type 2 diabetes and heart-related problems.
6. Inflammation Foods – Hydrogenated Oils and Trans Fat
Your body may become more prone to inflammation if hydrogenated vegetable oil contains trans fats [6]. Tran’s fat is present in most processed snack foods, frozen breakfast items, cookies, doughnuts, crackers, and fried fast food items. It is also known to cause systemic inflammation. Therefore, you should avoid food products that list partly hydrogenated oils among their ingredients.
7. Inflammation Foods – Dairy Products
People who are allergic to dairy products should avoid them as they can lead to inflammation in their bodies [7]. Even a tiny amount can trigger inflammation if someone is allergic to it.
8. Inflammation Foods – Excessive Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Although the body needs omega-6 fatty acids for many physiological processes, an unbalanced ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids can cause inflammation [8]. While omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids are required for health, an excessive consumption of omega-6, especially in the absence of sufficient omega-3, can contribute to developing pro-inflammatory eicosanoids.
9. Inflammation Foods – Excessive Alcohol
Your body produces several inflammatory chemicals during the breakdown of alcohol. Inevitable byproducts that it leaves behind have the potential to harm the liver, the stomach, and other organs. The body responds to this injury by becoming inflamed [9].
Why These Foods Can Cause Inflammation?
Now that we have seen the list of foods that may cause inflammation, it is time for us to understand the cause.
1. Imbalances in Gut Microbiota
Inflammation can be caused by dysbiosis, or imbalances in the gut microbiota, in several ways [10]. Trillions of bacteria called gut microbiota live in the digestive tract and are essential for the immune system, inflammatory management, and general health maintenance.
Toxins and germs are kept out of the bloodstream by the intestinal lining, a barrier. A weakened gut barrier brought on by dysbiosis may permit the translocation of dangerous substances and set off an inflammatory and immunological reaction.
2. Oxidative Stress
The body’s oxidative stress and inflammation processes are linked, and each can cycle back on the other [11]. When the body defences against or reparations for the damage caused by ROS, reactive oxygen species are disrupted, and oxidative stress results.
Free radicals, which are reactive oxygen species produced under oxidative stress, can harm DNA, lipids, and proteins in cells. The immune system responds to this harm by expelling damaged cells and starting healing procedures.
3. Allergies and Food Sensitivities
Inflammation can be brought on by food sensitivities and allergies, which are immune system reactions to things that the body perceives as dangers [12]. The immune system perceives specific food proteins, or allergens, as dangerous intruders in cases of allergies and sensitivities. This sets off an immunological reaction, which involves the activation of immune cells such as basophils and mast cells.
4. Pro-Inflammatory Compounds
Pro-inflammatory substances cause and intensify the body’s immunological response, leading to inflammation [13]. Many items include these chemicals, such as specific diets, ambient elements, and even endogenous molecules.
Extended exposure to these compounds has been associated with several inflammatory conditions, including metabolic disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and autoimmune diseases.
5. Imbalance between Omega 3 and Omega 6 Fatty Acids
Inflammation in the body may be caused by an imbalance in the diet between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids [14]. While both kinds of fatty acids are necessary for many physiological functions, a balanced and healthy inflammatory response depends on the ratio between the two.
6. Additives and Preservatives
Specific food additives and preservatives have been linked to the possibility of causing inflammation [15]. Although some people may not be susceptible to them, others may have adverse reactions, including inflammation.
Certain additives and preservatives may also trigger hypersensitive immunological responses in certain people, which can activate immune cells and cause the release of pro-inflammatory mediators. This immune system activity may start inflammation.
How do you Know about Inflammation?
1. Understanding Inflammation
It might appear as a swelling, redness, loss of function, heat, and pain that resemble the body’s healing process like after an injury or sickness [16]. However, you should get it checked if these symptoms do not go away after a few days.
2. Symptoms and Experiences
Inflammation that persists for long causes fatigue, pain, and higher disease susceptibility. It may seem like a lingering mild fever. This causes discomfort and is an indication of abnormalities in the normal functions of the body.
3. Health Conditions Linked to Inflammation
Inflammation can lead to severe health complications like arthritis and heart disease [18].
Diet and Lifestyle to Reduce Inflammation
- Mind Food Sensitivities: Knowing how your body reacts to different types of food is a useful weapon in combating inflammation. Be aware of reactions and try to avoid triggers; thus, improving the overall quality.
- Sound Sleep: Quality sleep – 7 to 9 hours each night is very critical for body repair, and it plays an important role in inflammation control[20]. Focusing on getting a good night’s rest helps promote overall wellness.
- Exercise: As well as a tune-up for the whole human body, regular exercise helps to minimize inflammation and make the functioning of the organism smooth[21]. A sort of sport which could be anything from just a stroll to hard training makes people balanced.
- Stay Hydrated: Being a common superhero, the water makes sure that the balance remains in control by getting rid of poisonous adulterants from within our bodies. Hydration is also a must for any anti-inflammatory treatment or other life support proceedings [22].
- Maintain a Healthy BMI: Weight is another vital aspect of healthy living [23].
- Consume Foods Rich in Antioxidants: Antioxidants in vegetables and fruits of diverse hues are powerful enough to fight inflammations [24]. Therefore, the usage of these foods in the diet enhances natural organisms’ resistance towards inflammations.
- Reduce Added Sugars: Alternatively, the lack of such sugary sweetness and drinks is another means by which something can gradually take away points that cause inflammation. In-between use together with low added sugar also could enable other aims for instance limited inflammation and overall equilibrium [25].
- Consume Lean Protein: The attractive lean proteins, however, are chicken fish and legumes that go through the working process without any inappropriate inflammation. These proteins are determined as the basis of a healthy and pro-inflammatory lifestyle.
Final Words
The key to a healthier life is understanding and controlling inflammation. Individuals can empower themselves through mindful dietary choices, adequate rest, regular exercise and taking a more holistic approach to living that will help them navigate the necessary balance which constitutes overall well-being plus prevention of various inflammatory-related health problems.
FAQs
Inflammation is a factor contributing to fatty liver, heart disease and some cancers. It functions as a driving force that worsens other medical problems.
Water is a superhero, getting rid of toxins and restoring equilibrium in the body. Hydration is very important to help control inflammations that also support the functioning of various organs in our bodies.
The awareness of how your body responds to the food also contributes to finding and eliminating possible triggers, thereby improving your overall well-being.